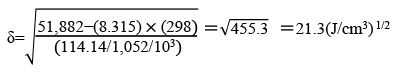High polar and aprotic solvent
DMI™ (1,3-Dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone)
1,3-Dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone
Applications detail
Applications
- Basic Information
- Details of Characteristics
- Details of Applications
Product Overview
DMI™ is an aprotic solvent with high polarity. DMI™ is used in a wide range of fields for its excellent dissolving power, stability, and high quality
Substance
| Chemical Name | Synonyms | CAS No. |
|---|---|---|
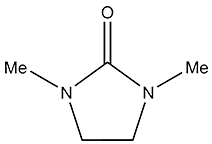
| 1,3-Dimethyl-2-Imidazolidinone | DMEU Dimethylethyleneurea | 80-73-9 |
Structural Formula
 1,3-Dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone
1,3-Dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone
1. Solvent for reaction
With its high dielectric constant and solvation effect, DMI™ accelerates anionic nucleophilic reactions, and reactions that place with solvation of cation.
DMI™ is thermally and chemically stable with excellent dissolving power for organic and inorganic compounds.
Since DMI™ is extremely useful as a reaction solvent, it is used in various reactions to synthesize medical drugs and pesticides.
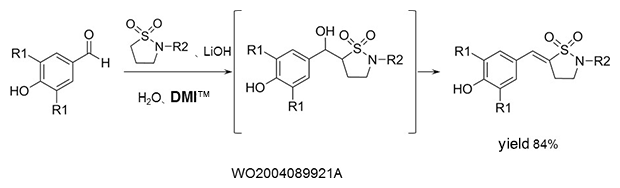
Aldol condensation
As a reaction solvent in the production of benzylidene derivatives that are used as anti-inflammatory agents.
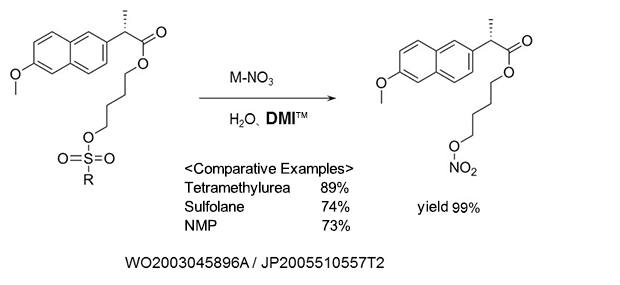
Nitric acid esterification
As a reaction solvent in the production of (S)-naproxen-4-nitroxybutyl ester used as anti-inflammatory agents, and analgesics.
Alkylation
(1) As a reaction additive in the production of alkyl compounds of γ-butyrolactone.
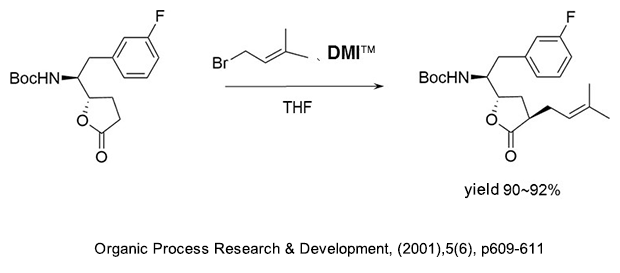
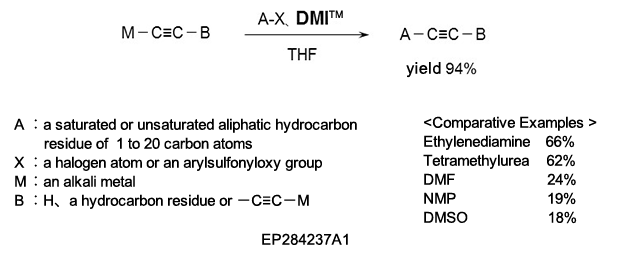
(2) As a reaction additive in the production of substituted acetylene compounds used as pharmaceutical intermediates.
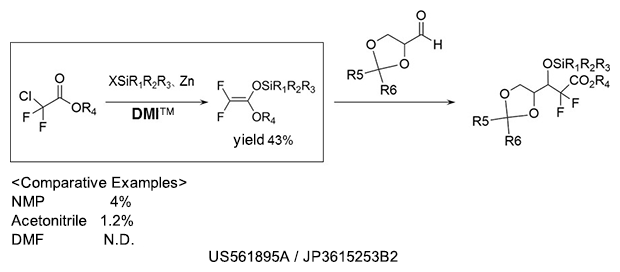
Silyl etherification
As a reaction solvent in the production of silyl ether compound used as pharmaceutical intermediates.
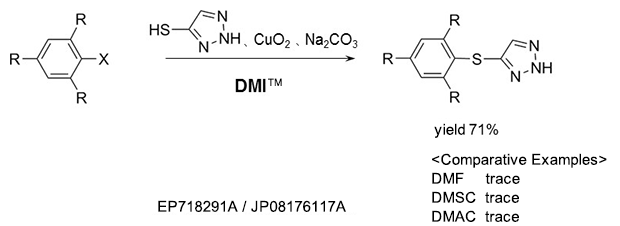
As a reaction solvent in the production of triazole derivative used as an herbicide.
As a reaction solvent to produce tetrafluoroethoxybenzenes used as intermediates for germicides, antibacterial agents, insecticides, and herbicides.
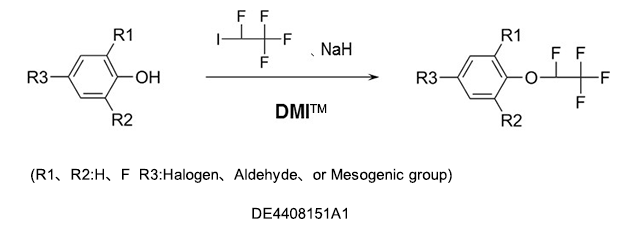
DMI™ improves the reactivity with its excellent solubility, cation solvation, and suppresses side reactions because of its high stability at high temperatures and in the presence of alkalis.
- In the production of polyamides and polyimides, DMI™ accelerates the formation of amide and imide groups to produce high molecular weight polymers.1)
- Polymers suitable for electronic parts with less ionic impurities can be obtained in the production process of polyphenylene sulfide.2)
- DMI™ can suppress side reactions in the production process of polyethersulfone to produce high quality polymers.3)
- DMI™ treatment during film formation of polyimide, stretching of polyether ketone film, and production of polysulfone membrane produces uniform and excellent quality products.4)
1)JP63108027A, JP 05140308A
2)JP63268740A
3)JP0586186A
4)JP61195130A, JP0313314A, JP6219209A
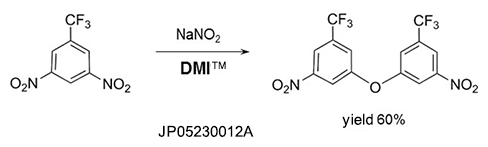
Phenyl ethers
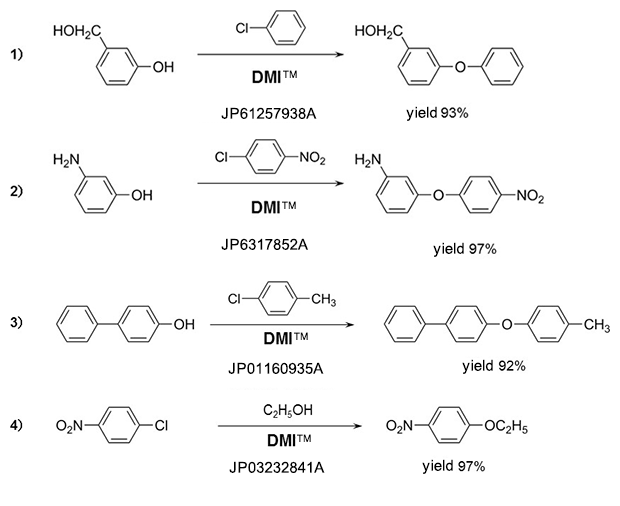
Amines
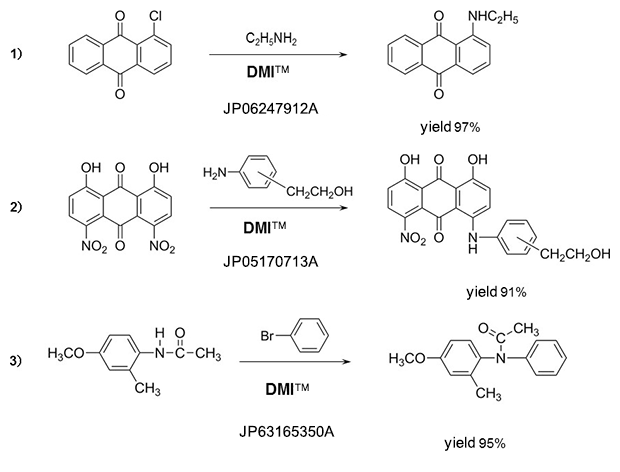
Fluorobenzenes
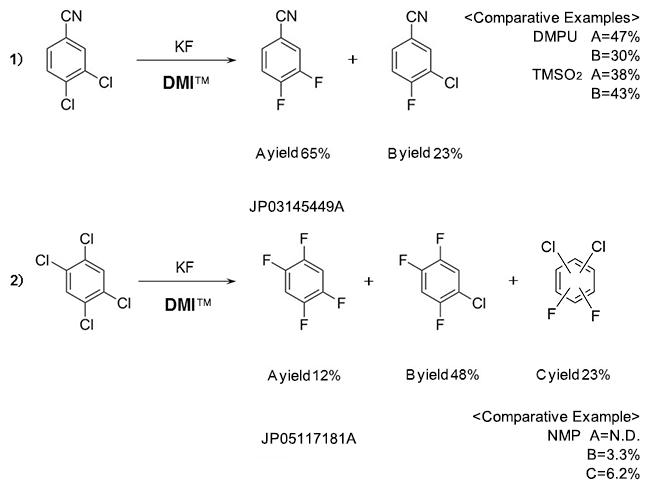
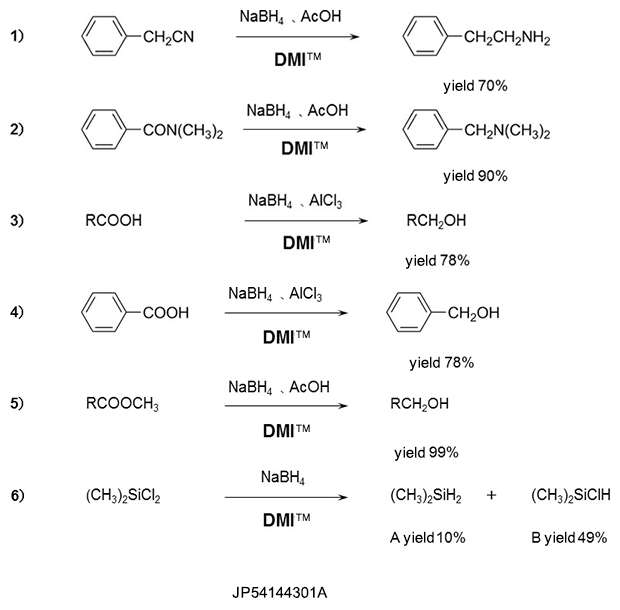
Reduction
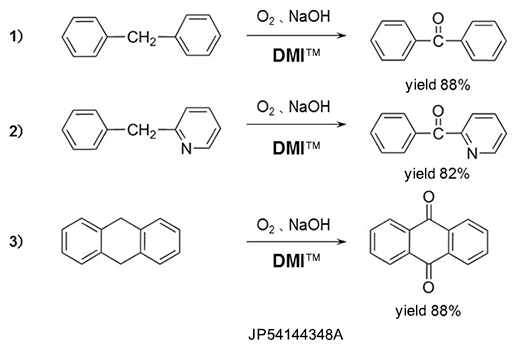
Oxydation
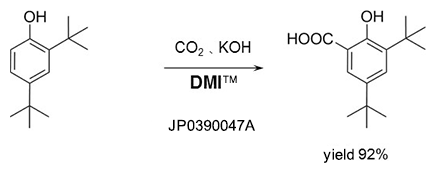
Kolbe-Schmitt reaction
Self-condensation
Dimerization
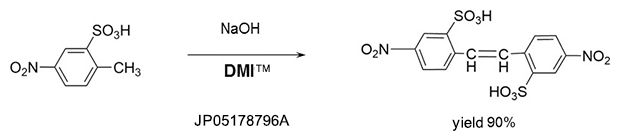
Addition reaction
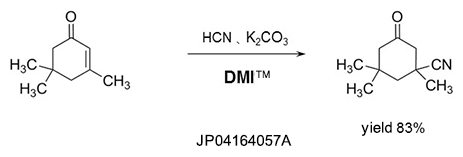
Dehydrating agent
DMI™ reacts with halogenating reagents such as phosgene, oxalyl chloride, and is effective as a dehydrating agent.
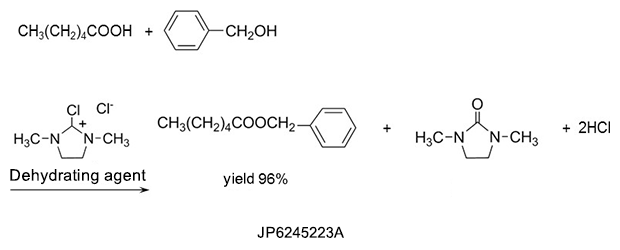
2. Detergents
DMI™ has strong dissolving power and is used in detergents such as paint peeling agents and photoresist stripping agents.5)
5)JP0715111A, JP06228591A
Paint peeling agents
A patent example for DMI™ used in paint peeling agents of acrylic, melamine, urethane type resins, which have sufficient paint removability and excellent workability.
The results after the evaluation test is shown in the table with number of changes for each of the following, ⊚ when changes are observed in the coating and primer resin; O, when the primer resin peels off by disintegration or swelling; Δ when peeling off is observed by partial dissolution or disintegration or swelling; X when no changes are observed (5 test samples were used)
| Detergents | Composition (wt%) | Temperature (℃) | Results | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ◎ | 〇 | △ | × | |||
| DMI™/EtOH | 90/10 | 50~100 | 5 | |||
| Methylene Chloride | 100 | 40 | 3 | 2 | ||
| DMF | 100 | 50~100 | 3 | 2 | ||
| DMSO | 100 | 50~100 | 4 | 1 | ||
※Acrylic curable paint with melamine coated on parts of polyolefin resin with primer
(Coating I and coating II have different chemical compositions for the coating and primer resins.)
6)JP2924323B2
Photoresist Stripping Agents
A patent example in which DMI™ has been used for photoresist stripping agents that are not corrosive to silver and silver alloys and has high peelability for photoresist and photoresist deteriorated layers7)
| Photoresist Stripping Agents | Composition (mass%) | Results | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Photoresist Peelability | Photoresist alteration layer Peelability | Corrosive to silver alloys | ||
| DMI™/2-(2-Aminoethoxy)ethanol | 70/30 | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ |
| DMI™/Monoethanolamine | 70/30 | ◎ | ◎ | × |
| DMI™/Triethanolamine | 70/30 | × | × | ◎ |
| DMI™/N,N-Diethanolamine | 70/30 | ○ | × | ◎ |
| DMI™/2-(2-minoethoxy)ethanol/Water | 60/30/10 | ◎ | × | × |
※Peelability:◎= Eliminable,○=Slight remaining,×= not eliminable
※Corrosive :◎=Remain the same,○=Discolored parts occur,
×= Discolored ・gloss level variation・stripped membranes parts occur
【Test Method】
The substrate used for evaluation was subject to dry etching and then immersed in a photoresist stripping agent at 70℃ for 10 minutes, and the peelability was evaluated using optical and electron microscopes.
Silver alloy corrosivity: A silver alloy formed on a glass substrate was immersed in a photoresist stripping agent at 70℃ for 10 minutes and evaluated for corrosivity using optical and electron microscopes.
7) WO2005/022268A1
3. Additives
DMI™ is used as an additive for adhesives, rubber processing aids, and electrolytes.
Adhesives
A patent example in which proper shape is retained, bonding duration is retained without decreasing the initial tack, has excellent and powerful adhesiveness that even bonds with coated paper for which adhesion is difficult, and used in the stick adhesive that has polyvinyl pyrrolidone as the main component.8)
| Example1 | Example2 | Example3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adhesive ingredienta) | 95% | 95% | 95% |
| Additive | DMI™ 5% | ε-Caprolactam 5% | None |
| Bonding strength test resultb) | 100% | 90% | 30% |
| Hardness test resultc) | 1.01 | 1.51 | 0.98 |
※a)Adhesive composition: 27% of polyvinyl pyrrolidone, 8% of sodium stearate, 50% of water, and 10% of glycerin
※b)Bonding strength test: Breaking rate of paper when high quality papers are stuck together and peeled after 3 days
※c)Hardness: Penetration distance (mm) by a 12.5 g needle in 10 seconds. Smaller the penetration distance, greater the hardness
8)JP11189757A
Rubber Processing Aids
A patent example of use in a modifying agent of rubber processing aids that can avoid deterioration of rebound resilience due to addition of processing aids, and deterioration in processability due to dispersion of carbon black. Evaluation of extrusion processability using a rubber composition according to the ASTM D2230-77A method
| Denaturant | Weight average molecular weight of liquid rubber | Additive amount of liquid rubbera) | 60℃ Repulsiveb) | Wetskid resistancec) | Extrusion processability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMI™ | 6,000 | 10 | 59 | 61 | 16 |
| None | 6,000 | 10 | 55 | 58 | 12 |
a)The amount of liquid rubber added is based on 100 g of SBR
b)The test specimen exposed to the atmosphere at 60℃ was measured according to JIS K-6301
c)Measured using a portable skid tester on the road surface of ASTME-303-74 specifications at 23℃
(manufactured by Stanley UK)
9)JP03281645A
Electrolytes
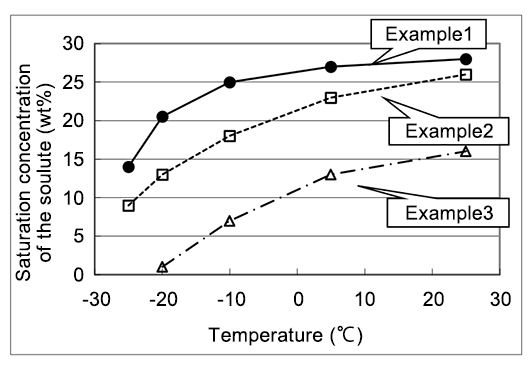
A patent example showing high specific conductivity and thermal stability, used as a solute precipitation inhibitor for electrolyte in which the solute of diazabicycloalkene carboxylate salt does not precipitate even at low temperatures10)
| Electrolyte composition(wt%) | Specific conductivity (30℃,ms/cm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | After the heat treatment | ||
| Example1 | Solute(25) γ-Butyrolactone(70) DMI™ (5) | 7.1 | 7.2 |
| Example2 | Solute(20) γ-Butyrolactone(65) Ethylene glycol(15) | 7.0 | 4.9 |
| Example3 | Solute(10) γ-Butyrolactone(90) | 4.5 | 4.5 |
Solute:Phthalic acid mono-1,5-Diazabicyclo[4.3.0]non-5-ene The heat treatment:150℃,10 hours
10)JP097895A
4. Solvent
When DMI™ is used as a solvent in the ink of inkjet printers, print density, drying resistance, and storage stability of the ink are known to improve.11)
11)JP04339873A, JP06172690A
5. Surface treatment agent
When the surface of the Teflon, a fluorine resin, is treated using a solution (etching agent) prepared by dissolving sodium, potassium, and lithium metal polyallyl complex dispersion is dissolved in DMI™, the bonding strength of epoxy resin adhesive improves.12)
12)JP5484501A
All references to the possible uses of our products contained in this brochure are made without any warranty, either express or implied.
Nothing herein shall be construed as a representation that our products are fit for use in manufacturing finished product similar or identical to those products displayed herein or for any other purpose.
Our customers must ultimately decide on the use of our products based on their sole independent judgment without any reliance on this brochure.
Nothing herein shall be construed as permission or as recommendation for uses which might infringe valid patents.
(Including patent applications), whether existing now or in the future, or as extending a license under such valid patents.
Because the conditions and methods of use on the part of our customers are beyond our control, we disclaim any liability incurred in connection with the use of our products.
For the detailed safety information, please refer to Materials Safety Data sheet of DMI™.