Trajectory of transformation and challenges
1912-1953
Origin of
Mitsui Chemicals
Challenge to develop Japan’s first coal chemical industry
Mitsui Chemicals’ coal chemical operations date back to the completion of the Koppers (by-product recovery) coke oven in Omuta in 1912. Starting with the production of chemical fertilizers from by-products that had previously been discarded, we have manufactured a variety of chemical products and responded to the cutoff of chemical imports due to the war and the postwar food crisis. As such, our history of solving social challenges is the DNA that leads to the present.
1912
General situation
Industry trend
Mitsui Chemicals
1912
Mitsui Mining built Japan’s first Koppers coke oven to start full-scale chemical operations (now Omuta Works)
Cutting off of chemical imports
1914
Outbreak of World War I
Promoted domestic production of chemicals
1915
Started production of Japan’s first synthetic dye alizarin (Omuta)
1916
Started production of phenol (Omuta)
1918
End of World War I
1924
Started production of Japan’s first synthetic ammonia (now Shimonoseki Mitsui Chemicals)
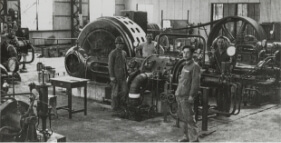
1932
Started production of synthetic dye indigo (Omuta)
1939
Outbreak of World War II
Severe postwar food crisis
1945
End of World War II
Increased chemical fertilizer production to end the food crisis
1948
Started Japan’s first mass production of urea for fertilizer (now Hokkaido Mitsui Chemicals)
Domestic production of petrochemical products promoted as a national policy
1950-
Energy revolution
Rapid increase in imports of synthetic resins, etc.
1954-2019
The Turning Point
of Mitsui Chemicals
Challenge to develop Japan’s first petrochemical industry
In line with the postwar energy revolution from coal to petroleum, Mitsui Chemicals was one of the first movers to adopt cutting-edge technologies in Europe and the U.S. and made a full-scale entry into the petrochemical industry. Completed in 1958, Japan’s first integrated petrochemical complex supported Japan’s rapid economic growth period.
The oil crisis broke out as we were steadily expanding our petrochemical business. In the course of getting through this crisis, we shifted our focus to high-value-added products and created a number of core businesses that support the Mitsui Chemicals Group today.
The chemical industry then entered an era of further intensified international competition. Following the global recession triggered by the collapse of Lehman Brothers and the launch of large-scale commodity products plants in China, the Mitsui Chemicals Group has been restructuring its business and transforming its portfolio under a new business plan.
1954
General situation
Industry trend

Number of ethylene crackers
Prepared based on data from the Japan Petrochemical Industry Association
Mitsui Chemicals
1954
Decided to enter the polyethylene business after meeting with Dr. Ziegler (Nobel Prize winner)

1955-
Period of the rapid economic growth
1955
Established Mitsui Petrochemical Industries
Driving a period of rapid economic growth
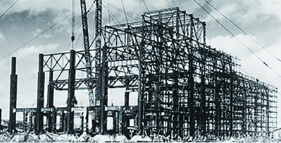
1958
Started operations at the Iwakuni Works (now Iwakuni-Ohtake Works), Japan’s first petrochemical complex

1962
Manufactured polypropylene for the first time in Japan (Iwakuni-Ohtake)
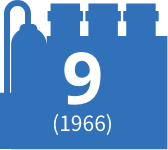

1967
Started production of ethylene at the Chiba Works (now Ichihara Works)

1968
Toyo Koatsu Industries and Mitsui Chemical Industry merged to form Mitsui Toatsu Chemicals
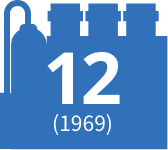

1970
Ethylene plant completed by Ukishima Petrochemicals* (Ukishima) (now ENEOS Corporation Kawasaki Refinery)
Started production of ethylene at Osaka Petrochemicals (Osaka)
A joint venture between Nippon Petrochemicals (now ENEOS Holdings, Inc.) and Mitsui Petrochemical Industries
1973
Outbreak of the first oil crisis
1978
Ethylene plant completed at Ukishima Petrochemicals (Chiba) (now Ethylene Plant at the Ichihara Works)
1979
Outbreak of the second oil crisis


1985
No. 3 Ethylene Plant at the Iwakuni-Ohtake Works suspended (complete shutdown in 1993)

1997
Asian currency crisis
Accelerated restructuring in the chemical industry
A series of giant companies emerged through M&A in the Western economies.
1997
Mitsui Petrochemical Industries and Mitsui Toatsu Chemicals merged to form Mitsui Chemicals
Promoting a shift to high-value-added products
Products developed in this period
1975: TAFMER™ / 1987: MR™, TREBON™, ICROS™ Tape / 1995 APEL™
Late 1980s - 1990s
Established sites in Singapore, the U.S., Europe, and China


Global recession
2008
Collapse of Lehman Brothers
A series of large-scale commodity chemicals plants started their operations in China.
2009
Sankyo Agro and the agrochemicals business of Mitsui Chemicals merged to form Mitsui Chemicals Agro (now Mitsui Chemicals Crop & Life Solutions)

2010
The film and sheet businesses of Tohcello and Mitsui Chemicals Fabro merged to form Mitsui Chemicals Tohcello (now Mitsui Chemicals ICT Materia)
2013
Acquired Heraeus Holding GmbH’s dental materials business

2015
SDGs adopted at UN Summit
COP21 decided on an international framework for reducing greenhouse gas emissions

2014-2016
Mid-Term Business Plan
2017-2021
Long-Term Business Plan VISION 2025
Restructuring/volatility reduction
2020-
Prospects for
the Future
Challenges to achieve a sustainable society
The history of the Mitsui Chemicals Group is truly a history of solving social challenges through technology innovation, from the challenge to develop the coal chemical industry in the first generation to the shift from coal to petroleum in the second generation. Now, carbon neutrality and the circular economy are being touted as challenges for the entire planet, and we are entering a period of great change that should be called the third generation. As a first mover, the Mitsui Chemicals Group aims to contribute to a sustainable society. We will accelerate the progress through collaboration and co-creation with other companies in addition to our power of chemistry.
Currently, there are 12 crackers in Japan. The external environment is changing by the minute, including environmental changes due to the friction between the U.S. and China, inflation, and other factors, as well as changes in the domestic market structure due to oversupply resulting from capacity expansion in China. We will proceed with the second phase of restructuring by identifying derivatives in view of product competitiveness, essential demand, which also considers economic security, and capital efficiency.
2020
General situation
Industry trend
Mitsui Chemicals
2020
Spread of COVID-19
2020
The Japanese government announced that it would achieve carbon neutrality by 2050.
Accelerated efforts toward a sustainable society
2020
Declared to be a carbon-neutral company by 2050
2021
Started production of Japan’s first bio-based plastics from bio-based hydrocarbons

2021-
Long-Term Business Plan VISION 2030
Promoting the second phase of restructuring and bolstering downstream businesses
Chemical complex transformation
Building solutions-based business models
Trends in Japan’s ethelene production
- Japan’s ethylene production*1 (right axis)
- Ethylene exports*2 (right axis)
- GDP*3 (left axis)
*1 & 4: Prepared based on data from the Japan Petrochemical Industry Association
*2: Prepared based on data from Trade Statistics of Japan published by the Ministry of Finance
*3: Prepared based on data from the Cabinet Office



